agent-workflow-memory
Basic Information
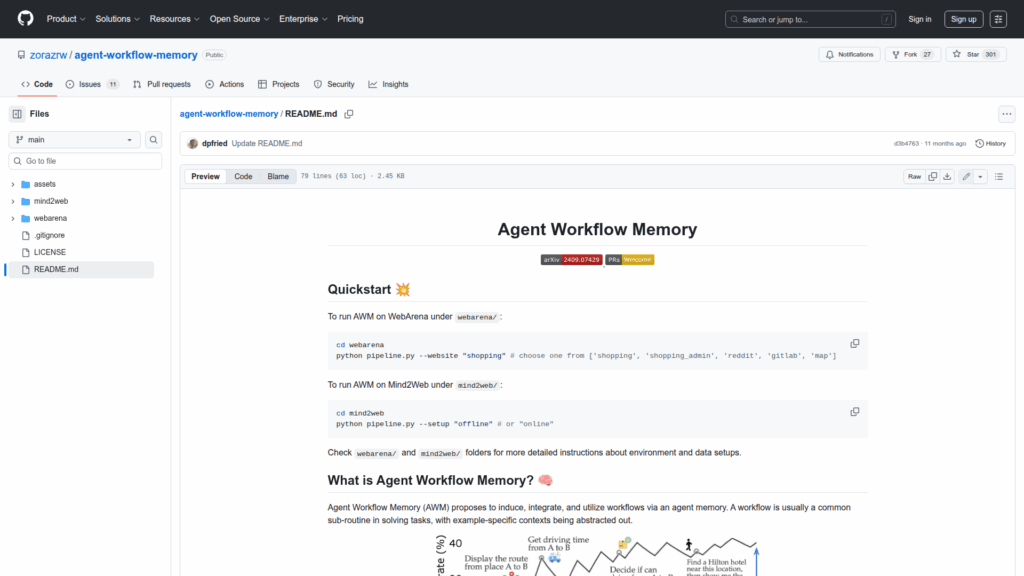
This repository implements Agent Workflow Memory (AWM), a research codebase and experimental toolkit for inducing, integrating, and utilizing reusable workflows inside agent systems. The project presents methods to extract common sub-routines (workflows) from examples or past agent experiences and to attach those workflows to agent memory to improve task solving. It includes runnable pipelines and environment-specific code for two evaluation settings, WebArena and Mind2Web, with instructions to run offline and online modes. The repo enables reproduction of the AWM paper's experiments, provides assets and result figures, and exposes scripts to run the provided pipelines for different websites or setups. The primary goal is to demonstrate a memory-driven workflow induction approach and provide the code necessary for researchers to evaluate and extend the method.