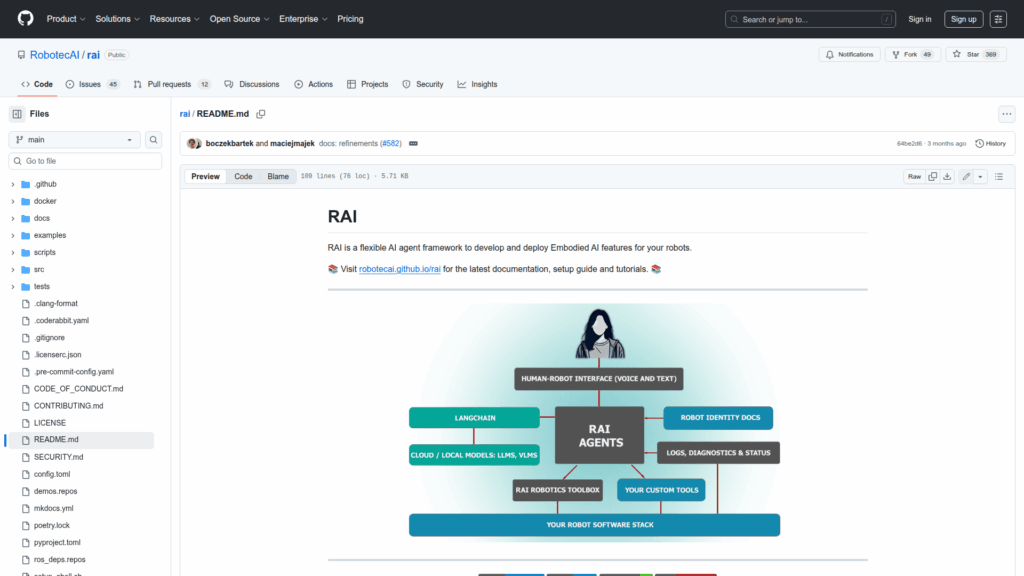
Basic Information
RAI is a flexible, vendor-agnostic framework designed to develop and deploy embodied AI capabilities on robots. It provides infrastructure for building multi-agent systems that enable natural human-robot interaction, multimodal perception and action, and scenario-driven behaviors. The repository bundles core components, tooling and demos to connect AI models, sensors and simulators to real or virtual robots. It targets robotics developers, researchers and integrators who want to add generative AI features, speech interfaces, perception modules and navigation support into robotic platforms. Documentation, setup guides and community resources are provided to help teams configure RAI for a specific robot embodiment, run simulation demos, and evaluate agents with benchmarking tools. The project emphasizes modularity so users can adopt individual packages such as ASR, TTS, simulation connectors or benchmark suites while integrating into an existing robotics stack.